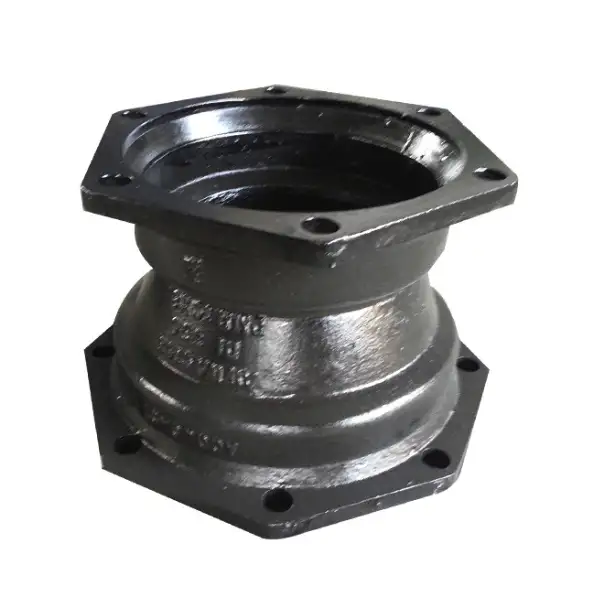
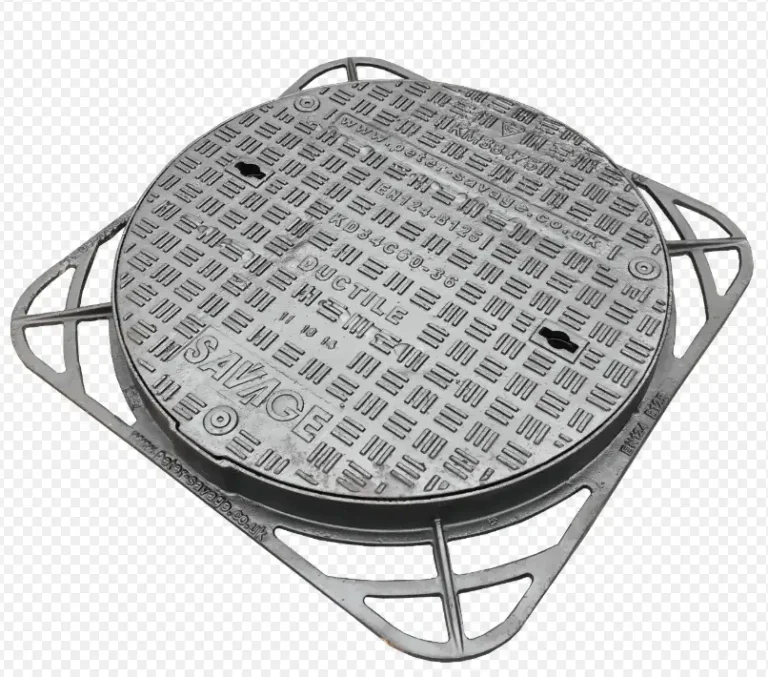
تركيبات الوصلات الميكانيكية المصنوعة من حديد الدكتايل هي مكونات أساسية في البنية التحتية للمياه والصرف الصحي. فهي توفر وصلة موثوقة ومرنة بين الأنابيب، وتستوعب الحركة وتقلل من مخاطر التسريبات. تُستخدم هذه التركيبات على نطاق واسع في التطبيقات البلدية والصناعية والتجارية نظراً لمتانتها وسهولة تركيبها.
التطور التاريخي والمعايير
يعود تاريخ تطوير الوصلات الميكانيكية المصنوعة من حديد الدكتايل إلى أوائل القرن العشرين. وقد وضعت الجمعية الأمريكية لأشغال المياه (AWWA) معايير مثل ANSI/AWA C110/A21.10 و ANSI/AWA C111/A21.11 لضمان التوحيد والجودة في التصنيع. وبمرور الوقت، تم تحديث هذه المعايير لدمج التطورات في المواد والتكنولوجيا.
تركيبة المادة ومواصفاتها
تُصنع تركيبات الوصلات الميكانيكية المصنوعة من حديد الدكتايل المصنوعة من حديد الدكتايل في المقام الأول، وهي مادة معروفة بقوتها ومرونتها. وتشمل المواصفات ما يلي:
-
درجة المادة: ASTM A536
-
تصنيف الضغط: عادةً 350 PSI للمقاسات من 3″ إلى 24″، و250 PSI للمقاسات من 30″ إلى 48″
-
الطلاءات: بطانة من الأسمنت والملاط مع طلاء إسفلتي لمقاومة التآكل
-
الحشيات: متوافق مع معايير ANSI/AWA C111/A21.11
ميزات ومكونات التصميم
يتضمن تصميم تركيبات الوصلات الميكانيكية المصنوعة من حديد الدكتايل عدة مكونات رئيسية:
-
الغدة: مكون من حديد الدكتايل الذي يضغط على الحشية
-
حشية: عنصر مطاطي يوفر مانع تسرب الماء
-
البراغي والصواميل: مكونات من سبائك الصلب التي تثبت الغدة
-
الجسم المناسب: الجسم الرئيسي للتركيبة، الذي يتصل بالأنبوب
تعمل هذه المكونات معاً لإنشاء مفصل آمن ومرن.
التطبيقات في أنظمة المياه والصرف الصحي
تُستخدم تركيبات الوصلات الميكانيكية المصنوعة من حديد الدكتايل في تطبيقات مختلفة:
-
أنظمة توزيع المياه: توصيل الأنابيب في شبكات إمدادات المياه البلدية
-
أنظمة الصرف الصحي: ضمان التوصيلات المانعة للتسرب في أنابيب مياه الصرف الصحي
-
أنظمة الحماية من الحرائق: توفير اتصالات موثوقة في البنية التحتية لإخماد الحرائق
تعدد استخداماتها يجعلها مناسبة لكل من التركيبات فوق الأرض وتحت الأرض.
إجراءات التثبيت وأفضل الممارسات
التركيب السليم أمر بالغ الأهمية لأداء تركيبات الوصلات الميكانيكية المصنوعة من حديد الدكتايل:
-
التحضير: نظف أطراف الأنابيب وتأكد من خلوها من الحطام
-
وضع الحشية: قم بتشحيم الحشية ووضعها بشكل صحيح
-
تجميع الغدة: مرر الغدة على الأنبوب وحاذيها مع الحشية
-
شد البراغي: أحكم ربط المسامير تدريجيًا بنمط متقاطع لضمان الضغط المتساوي
يضمن اتباع هذه الخطوات الحصول على وصلة آمنة وخالية من التسرب.
الصيانة واستكشاف الأعطال وإصلاحها
تعمل الصيانة الدورية على إطالة العمر الافتراضي للتركيبات الميكانيكية المصنوعة من حديد الدكتايل:
-
الفحص: افحص دوريًا بحثًا عن علامات التآكل أو التآكل
-
التشحيم: ضع مادة تشحيم على الحشيات أثناء التركيب لمنع التلف
-
عزم دوران البرغي: تأكد من إحكام ربط البراغي حسب مواصفات الشركة المصنعة
في حالة حدوث تسربات، تحقق من عدم محاذاة الحشية أو تلفها واستبدلها حسب الضرورة.
المزايا مقارنة بأنواع المفاصل الأخرى
توفر تركيبات الوصلات الميكانيكية المصنوعة من حديد الدكتايل العديد من المزايا:
-
المرونة: استيعاب حركة الأنابيب بسبب التحولات الأرضية أو التمدد الحراري
-
سهولة التركيب: لا تتطلب أدوات أو معدات خاصة
-
المتانة: مقاومة للتآكل والتآكل
-
الفعالية من حيث التكلفة: توفير حل موثوق به بسعر تنافسي
هذه المزايا تجعلها الخيار المفضل في العديد من التطبيقات.
الاعتبارات البيئية
تجهيزات الوصلات الميكانيكية المصنوعة من حديد الدكتايل صديقة للبيئة:
-
قابلية إعادة التدوير: مصنوعة من مواد قابلة لإعادة التدوير
-
مقاومة التآكل: تقليل الحاجة إلى الاستبدال المتكرر
-
كفاءة الطاقة: عمليات التصنيع موفرة للطاقة
تساهم هذه العوامل في تطوير البنية التحتية المستدامة.
الاتجاهات والابتكارات المستقبلية
يشمل مستقبل تركيبات الوصلات الميكانيكية المصنوعة من حديد الدكتايل الميكانيكية ما يلي:
-
المراقبة الذكية: دمج أجهزة الاستشعار لمراقبة سلامة المفاصل
-
المواد المتقدمة: تطوير الطلاءات لتعزيز مقاومة التآكل
-
الأتمتة: استخدام الروبوتات في التصنيع من أجل الدقة والكفاءة
تهدف هذه الابتكارات إلى تحسين الأداء وتقليل تكاليف الصيانة.
الأسئلة الشائعة (FAQs)
1. ما هي تركيبات الوصلات الميكانيكية المصنوعة من حديد الدكتايل؟
تركيبات الوصلة الميكانيكية المصنوعة من حديد الدكتايل هي مكون يستخدم لتوصيل الأنابيب في أنظمة المياه والصرف الصحي. وهي تتألف من غدة وحشية ومسامير وجسم التركيبة، مما يوفر وصلة مرنة ومانعة للتسرب.
2. كيف يمكن مقارنة تركيبات الوصلات الميكانيكية المصنوعة من حديد الدكتايل بأنواع الوصلات الأخرى؟
مقارنةً بوصلات الدفع أو الوصلات ذات الحواف، توفر الوصلات الميكانيكية مرونة أكبر ويسهل تركيبها بدون أدوات خاصة. كما أنها فعالة من حيث التكلفة ومناسبة لمختلف التطبيقات.
3. ما هي معدلات الضغط للتركيبات الميكانيكية المصنوعة من حديد الدكتايل؟
عادةً ما تكون تركيبات الوصلات الميكانيكية المصنوعة من حديد الدكتايل ذات معدل ضغط يبلغ 350 PSI للأحجام من 3 إلى 24 بوصة و250 PSI للأحجام من 30 إلى 48 بوصة. تضمن هذه التصنيفات قدرة التجهيزات على تحمل الضغوط التي تواجهها أنظمة المياه والصرف الصحي.
4. هل يمكن استخدام تركيبات الوصلات الميكانيكية المصنوعة من حديد الدكتايل في التركيبات تحت الأرض وفوق الأرض؟
نعم، تركيبات الوصلات الميكانيكية المصنوعة من حديد الدكتايل متعددة الاستخدامات ويمكن استخدامها في كل من التركيبات تحت الأرض وفوق الأرض، مما يجعلها مناسبة لمجموعة كبيرة من التطبيقات.
5. ما هي الصيانة المطلوبة للتركيبات الميكانيكية المصنوعة من حديد الدكتايل؟
يعد الفحص المنتظم بحثًا عن علامات التآكل أو التآكل، وتزييت الحشيات أثناء التركيب، والتأكد من إحكام ربط البراغي وفقًا لمواصفات الشركة المصنعة من ممارسات الصيانة الأساسية لضمان طول عمر التجهيزات الميكانيكية لمفصل حديد الدكتايل.
6. هل تركيبات الوصلات الميكانيكية المصنوعة من حديد الدكتايل صديقة للبيئة؟
نعم، تركيبات الوصلات الميكانيكية المصنوعة من حديد الدكتايل مصنوعة من مواد قابلة لإعادة التدوير، ومقاومة للتآكل، ومصنعة باستخدام عمليات موفرة للطاقة، مما يساهم في تطوير البنية التحتية المستدامة.