Choosing the right type of water pipe is critical for ensuring the durability, safety, and efficiency of your plumbing system. Whether you’re working on a residential project, a commercial installation, or even an industrial setup, understanding the different types of water pipes is essential. In this guide, we’ll explore the most common types of water pipes, including ductile iron pipes, PVC, copper, and others, to help you make an informed decision.
Water pipes come in various materials, each offering unique benefits, costs, and potential drawbacks. We’ll cover these materials in-depth, compare them based on different factors, and answer the most frequently asked questions to ensure you make the best choice for your specific needs.
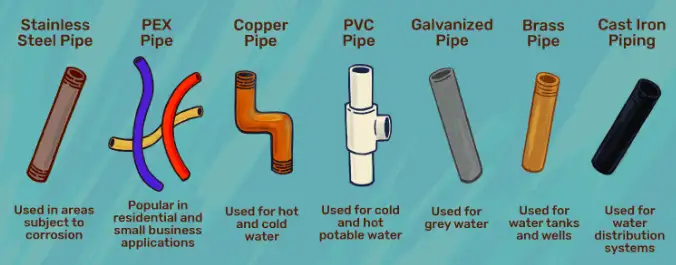
Types of Water Pipes: A Detailed Overview
1. Ductile Iron Pipes (DI Pipes)
Overview: Ductile iron pipes are made from iron that has been treated to improve its strength and ductility, allowing them to handle greater stress. They are typically used in large-scale water distribution systems, especially in areas with high water pressure or where the pipe needs to withstand environmental stressors.
Advantages:
-
Durability: Ductile iron pipes are known for their strength and long lifespan, often lasting for 50-100 years or more.
-
Resistance to Corrosion: These pipes are resistant to corrosion, especially when lined with protective coatings, making them ideal for use in both urban and rural environments.
-
High Pressure Handling: Due to their toughness, ductile iron pipes are capable of handling high-pressure systems without cracking or failing.
Disadvantages:
-
Weight: Ductile iron pipes are much heavier than other types of pipes, making them more difficult to transport and install.
-
Cost: These pipes tend to be more expensive than alternatives such as PVC or copper.
-
Prone to Cracking in Freezing Conditions: Although resistant to corrosion, ductile iron can still crack under extreme cold if not properly protected.
Best Use: Ideal for municipal water systems, large industrial projects, and areas with high water pressure or harsh environmental conditions.
2. PVC Pipes (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Overview: PVC pipes are a popular and cost-effective solution for residential water systems. They are made from a synthetic plastic polymer, which is lightweight, flexible, and easy to install. PVC is commonly used in irrigation systems, household plumbing, and sewage lines.
Advantages:
-
Affordable: PVC is one of the most affordable materials for water pipes, making it a great choice for budget-conscious projects.
-
Corrosion Resistance: PVC pipes do not rust, corrode, or degrade like metal pipes, which makes them a reliable long-term solution.
-
Lightweight: PVC pipes are much lighter than ductile iron, making them easier to transport and install.
Disadvantages:
-
Temperature Sensitivity: PVC can become brittle in extreme cold or high heat, which may cause cracking or breakage.
-
Lower Durability: While PVC is resistant to corrosion, it may not be as durable as materials like copper or ductile iron in the long term.
-
Not Ideal for High-Pressure Systems: PVC pipes are generally not recommended for systems with extremely high water pressure, as they can warp or break under stress.
Best Use: Ideal for residential plumbing, irrigation, and low-pressure systems.
3. Copper Pipes
Overview: Copper pipes have been used in plumbing for centuries and are known for their reliability, durability, and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. Copper is naturally resistant to corrosion and has antibacterial properties, making it a safe option for drinking water systems.
Advantages:
-
Longevity: Copper pipes can last 50 years or more with proper maintenance.
-
Antibacterial Properties: Copper has natural antibacterial properties that prevent the growth of harmful bacteria inside the pipes.
-
Heat Resistance: Copper can withstand both high and low temperatures, making it a versatile option for a variety of water applications.
Disadvantages:
-
Cost: Copper is one of the more expensive materials for water pipes, which can increase the overall cost of a plumbing project.
-
Corrosion in Acidic Water: Copper can corrode in water that has a high level of acidity, so it’s important to test the water before installing copper pipes.
-
Requires Skilled Installation: Copper pipes require more skill to install properly compared to PVC or PEX pipes, which may increase installation costs.
Best Use: Ideal for high-end residential plumbing, heating systems, and potable water distribution.
4. PEX Pipes (Cross-Linked Polyethylene)
Overview: PEX pipes are a relatively new type of plastic plumbing pipe that has gained popularity due to their flexibility, ease of installation, and resistance to both high and low temperatures. PEX is widely used in residential homes for water supply lines and heating systems.
Advantages:
-
Flexibility: PEX pipes can bend and curve, making them easy to install around corners and obstructions without the need for additional fittings.
-
Resistant to Freezing: PEX is more resistant to freezing and bursting than PVC or copper, making it a good choice for colder climates.
-
Affordable: PEX is relatively inexpensive compared to copper and ductile iron, which makes it a cost-effective option for homeowners.
Disadvantages:
-
Potential Chemical Leaching: There are concerns that PEX may leach chemicals into the water supply, although most modern PEX pipes are certified for potable water.
-
UV Sensitivity: PEX pipes should not be exposed to direct sunlight for long periods, as UV rays can degrade the material over time.
-
Less Durability in High-Pressure Systems: PEX pipes may not be suitable for very high-pressure water systems.
Best Use: Ideal for residential water supply lines, radiant heating systems, and low-pressure applications.
Comparison Table: Key Differences Between Water Pipe Materials
| Material | Durability | Cost | Resistance to Corrosion | Temperature Resistance | Pressure Resistance | Best Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ductile Iron | High | High | Very Good | Excellent | Very Good | Large-scale municipal systems, industrial applications |
| PVC | Moderate | Low | Excellent | Moderate | Low | Residential plumbing, irrigation systems |
| Copper | High | High | Excellent | Excellent | High | High-end residential plumbing, heating systems |
| PEX | Moderate | Moderate | Good | Excellent | Moderate | Residential water lines, radiant heating |
| Galvanized Steel | Moderate | Moderate | Fair | Moderate | High | Older homes, low-budget applications |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the best type of water pipe for residential plumbing?
When it comes to residential plumbing, the best water pipe depends on a variety of factors such as budget, climate, and personal preferences. For most homeowners, PEX is an excellent choice due to its flexibility, ease of installation, and affordability. PEX is particularly ideal for retrofitting older homes or running water supply lines around corners or obstacles. It’s also resistant to freezing, making it suitable for colder climates.
Another great option is copper, which, although more expensive, provides long-term durability, natural corrosion resistance, and antibacterial properties. If budget is a concern, PVC may be a good alternative for non-potable water lines or irrigation systems.
In cases where high pressure or large-scale systems are needed, ductile iron pipes may be the best choice, although they are typically reserved for municipal water systems due to their high cost and weight.
2. Are ductile iron pipes suitable for residential use?
While ductile iron pipes are often used in large-scale municipal water distribution systems, they can also be used for residential purposes in areas with specific needs, such as high water pressure or potential environmental stressors. Ductile iron pipes are extremely durable and resistant to corrosion, which makes them an excellent choice for situations where long-term performance is crucial. However, due to their weight and cost, they are not commonly used for regular home plumbing. They are better suited for industrial or commercial applications.
3. Can PVC pipes be used for drinking water?
Yes, PVC pipes are commonly used for drinking water applications, but only if they are specifically labeled as “potable” PVC. Potable PVC pipes are designed to meet safety standards for carrying drinking water and are manufactured with materials that do not leach harmful chemicals into the water. Non-potable PVC pipes, on the other hand, should only be used for applications such as drainage or irrigation, as they may contain substances that are harmful if ingested.
4. What factors should I consider when choosing a water pipe material?
When selecting the best water pipe for your needs, consider the following factors:
-
Budget: Some materials like PVC and PEX are much more affordable than others like copper or ductile iron.
-
Durability: If you’re looking for a long-lasting solution, consider materials like ductile iron or copper.
-
Climate: For colder climates, consider PEX, which is more resistant to freezing and bursting.
-
Installation Ease: PEX and PVC are easier to install compared to copper and ductile iron.
-
Water Pressure: For high-pressure systems, copper or ductile iron is typically preferred, as they can handle higher stress levels.
5. How long do different water pipes last?
The lifespan of water pipes varies depending on the material:
-
Ductile Iron: 50-100+ years, depending on environmental conditions.
-
PVC: 25-40 years, but may degrade under high pressure or extreme temperatures.
-
Copper: 50+ years, though it can corrode in acidic water conditions.
-
PEX: 40-50 years, with some brands offering warranties up to 25 years.
Conclusion
Choosing the best water pipe depends on your specific needs, budget, and installation conditions. Whether you opt for ductile iron, PVC, copper, or PEX, each material offers unique advantages and considerations. Always weigh the pros and cons carefully to ensure you select the most appropriate pipe for your project. Consulting with a professional plumber or contractor can also help you make the best decision based on your specific water system requirements.
References:
- AWWA C151: Standard for Ductile-Iron Pipe, Centrifugally Cast, for Water – American Water Works Association
- ISO 2531: Ductile iron pipes and fittings – Requirements and test methods – International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
- Copper Pipe Standards and Specifications – Plumbing Product Reviews
- PVC Pipes: Standards and Specifications – The Plastics Pipe Institute
- PEX Pipe: Advantages and Standards – PEX Connections
