In the realm of piping systems, ensuring secure and reliable connections is paramount. Two prevalent methods for joining pipes are mechanical joints and flanged joints. Understanding the distinctions between these two can significantly influence the efficiency, cost, and longevity of a piping system.
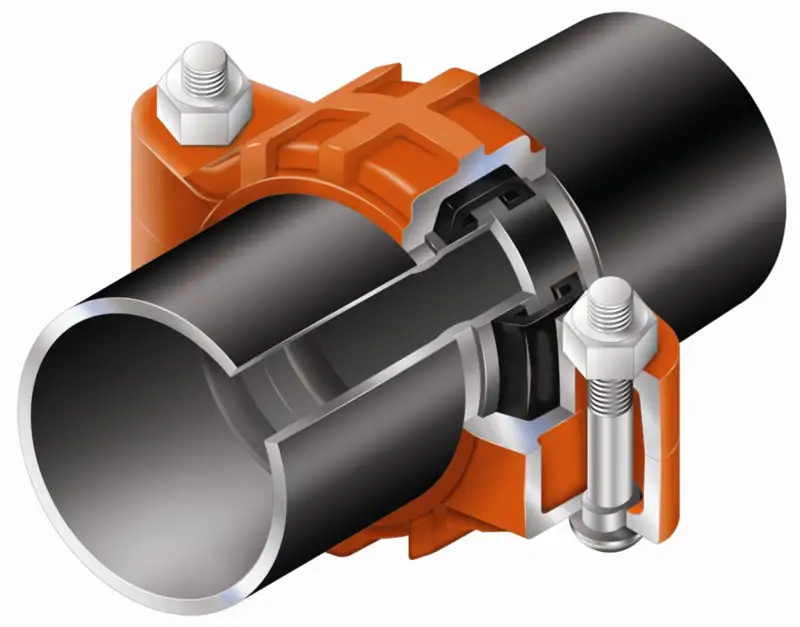
1. Overview of Mechanical Joints
Mechanical joints are a type of pipe connection that utilizes bolts, gaskets, and glands to create a watertight seal. They are designed to allow for some flexibility and movement between connected pipes, making them suitable for applications where slight misalignments or ground movements are expected.
Key Components:
-
Gland: A ring that compresses the gasket to form a seal.
-
Gasket: A rubber or elastomeric material that ensures a leak-proof connection.
-
Bolts: Fasteners that secure the gland and compress the gasket.
Advantages:
-
Flexibility: Accommodates minor misalignments and ground movements.
-
Ease of Installation: Faster and requires less labor compared to flanged joints.
-
Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive due to simpler components and installation.
Disadvantages:
-
Pressure Limitations: Not suitable for high-pressure applications without additional reinforcement.
-
Maintenance: May require more frequent maintenance checks to ensure integrity.
2. Overview of Flanged Joints
Flanged joints involve connecting pipes using flanges, bolts, and gaskets. The flanges are welded or threaded onto the pipe ends, and bolts are used to fasten them together, creating a rigid and secure connection.
Key Components:
-
Flanges: Flat pieces of metal with holes for bolts, welded or threaded onto pipe ends.
-
Bolts: Fasteners that secure the flanges together.
-
Gasket: Placed between flanges to ensure a leak-proof seal.
Advantages:
-
High Pressure Tolerance: Suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
-
Rigid Connection: Provides a strong and secure connection, ideal for critical systems.
-
Ease of Maintenance: Flanged connections are easier to disassemble for inspection or repair.
Disadvantages:
-
Installation Complexity: Requires precise alignment and skilled labor, making installation more time-consuming.
-
Cost: Generally more expensive due to materials and labor involved.
3. Comparison Table
| Feature | Mechanical Joints | Flanged Joints |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High | Low |
| Pressure Tolerance | Moderate | High |
| Installation Time | Short | Longer |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Maintenance | Requires regular checks | Easier to disassemble for maintenance |
| Applications | Underground pipelines, water distribution | High-pressure systems, industrial plants |
4. Applications of Mechanical Joints
Mechanical joints are commonly used in situations where flexibility and ease of installation are crucial. They are ideal for underground pipelines, water distribution systems, and areas prone to ground movement.
Typical Applications:
-
Water Distribution Systems: Ensures leak-proof connections in municipal water supply lines.
-
Sewer Systems: Accommodates ground shifts and settlements.
-
Industrial Applications: Suitable for systems requiring frequent disassembly and reconfiguration.
5. Applications of Flanged Joints
Flanged joints are preferred in high-pressure and high-temperature environments where a rigid and secure connection is necessary. They are commonly used in power plants, chemical processing industries, and HVAC systems.
Typical Applications:
-
Power Plants: Handles high-pressure steam and water systems.
-
Chemical Processing: Resists corrosion and withstands high temperatures.
-
HVAC Systems: Provides secure connections in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
6. Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Mechanical Joints:
-
Installation: Requires less time and labor; suitable for field installations.
-
Maintenance: Periodic checks are necessary to ensure gasket integrity and prevent leaks.
Flanged Joints:
-
Installation: Involves precise alignment and skilled labor; more time-consuming.
-
Maintenance: Easier to disassemble for inspection or repair; regular maintenance ensures longevity.
7. Cost Analysis
While mechanical joints are generally more cost-effective due to simpler components and installation, flanged joints may be more economical in the long term for high-pressure systems due to their durability and lower maintenance requirements.
8. Conclusion
The choice between mechanical joints and flanged joints depends on specific project requirements, including pressure conditions, flexibility needs, installation time, and budget constraints. Mechanical joints offer flexibility and ease of installation, making them suitable for underground and low-pressure applications. Flanged joints provide a rigid and secure connection, ideal for high-pressure and critical systems. Careful consideration of these factors will ensure the selection of the appropriate joint type for your piping system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the primary differences between mechanical joints and flanged joints?
Mechanical joints utilize bolts, gaskets, and glands to create a flexible and watertight seal, suitable for applications requiring movement accommodation. Flanged joints involve welding or threading flanges onto pipe ends, using bolts to secure them, providing a rigid connection ideal for high-pressure systems.
2. In what scenarios are mechanical joints preferred over flanged joints?
Mechanical joints are preferred in underground pipelines, water distribution systems, and areas prone to ground movement due to their flexibility and ease of installation.
3. What are the advantages of using flanged joints?
Flanged joints offer high-pressure tolerance, a rigid connection, and ease of maintenance, making them suitable for power plants, chemical processing industries, and HVAC systems.
4. How does the installation process differ between mechanical and flanged joints?
Mechanical joints require less time and labor for installation, suitable for fieldwork. Flanged joints involve precise alignment and skilled labor, making the installation process more time-consuming.
5. What are the cost implications of choosing between mechanical and flanged joints?
Mechanical joints are generally more cost-effective due to simpler components and installation. Flanged joints may have a higher initial cost but can be more economical in the long term for high-pressure systems due to their durability and lower maintenance requirements.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between mechanical and flanged joints is crucial for selecting the appropriate connection method for your piping system. By considering factors such as pressure conditions, flexibility needs, installation time, and budget constraints, you can ensure the longevity and efficiency of your system.

