In the world of cast iron materials, ASTM A126 and ASTM A536 are two prominent standards that cater to different industrial needs. While both fall under the cast iron category, they possess distinct characteristics that make them suitable for specific applications. Understanding the differences between these two standards is crucial for engineers, manufacturers, and procurement professionals to select the appropriate material for their projects.
1. Overview of ASTM A126
ASTM A126 is a standard specification for gray iron castings used in mechanical and pressure applications. It is primarily categorized into three classes:
-
Class A: Intended for use in steam and other high-temperature applications.
-
Class B: Designed for general-purpose applications.
-
Class C: Used for applications requiring higher strength.
These castings are characterized by their flake graphite microstructure, which provides excellent machinability and damping properties.
2. Overview of ASTM A536
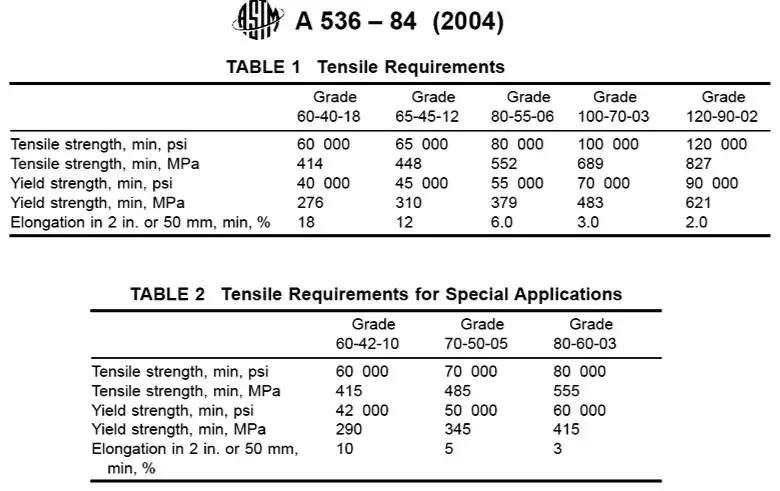
ASTM A536 is the standard specification for ductile iron castings, also known as nodular cast iron. This material is produced by adding a small amount of magnesium to molten iron, resulting in a microstructure of spheroidal graphite nodules. The primary grades under this standard include:
-
Grade 60-40-18: Offers a balance of strength and ductility.
-
Grade 65-45-12: Provides higher strength and moderate ductility.
-
Grade 80-55-06: Delivers superior strength and lower elongation.
Ductile iron is known for its improved mechanical properties compared to gray iron, including higher tensile strength and impact resistance.
3. Chemical Composition Comparison
| Element | ASTM A126 (Class B) | ASTM A536 (Grade 65-45-12) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon | 3.0% – 3.4% | 3.4% – 3.8% |
| Silicon | 1.8% – 2.8% | 2.5% – 3.0% |
| Manganese | 0.6% – 1.0% | 0.15% – 0.35% |
| Sulfur | ≤0.10% | ≤0.020% |
| Phosphorus | ≤0.08% | ≤0.060% |
This table highlights the variations in chemical composition between the two standards, influencing their respective properties and suitability for different applications.
4. Mechanical Properties Comparison
| Property | ASTM A126 (Class B) | ASTM A536 (Grade 65-45-12) |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 30,000 – 60,000 psi | ≥65,000 psi |
| Yield Strength | Not specified | ≥45,000 psi |
| Elongation | 1.5% – 3.0% | ≥12% |
| Hardness | 170 – 220 HB | 131 – 220 HB |
| Impact Resistance | Low | High |
The mechanical properties of ASTM A536 generally surpass those of ASTM A126, offering higher strength and better ductility.
5. Microstructure Differences
-
ASTM A126: Features a flake graphite structure, which provides excellent damping capacity but lower tensile strength and impact resistance.
-
ASTM A536: Exhibits a spheroidal graphite structure, resulting in improved tensile strength, ductility, and impact resistance.
These microstructural differences significantly affect the performance characteristics of the materials.
6. Applications and Industry Usage
| Application Area | ASTM A126 (Class B) | ASTM A536 (Grade 65-45-12) |
|---|---|---|
| Valve Bodies and Bonnet | Yes | Yes |
| Pump Components | Yes | Yes |
| Automotive Parts | No | Yes |
| Structural Components | No | Yes |
| Heavy Machinery | No | Yes |
While both materials are used in valve bodies and bonnets, ASTM A536 is more prevalent in applications requiring higher strength and impact resistance.
7. Cost Considerations
Generally, ASTM A536 materials are more expensive than ASTM A126 due to their superior mechanical properties and the additional processing required. However, the enhanced performance can lead to cost savings in applications where durability and reliability are critical.
8. Environmental and Sustainability Aspects
Ductile iron (ASTM A536) is considered more environmentally friendly compared to gray iron (ASTM A126) due to its lower carbon footprint during production and longer service life, reducing the frequency of replacements.
9. Global Standards and Equivalents
| ASTM A126 (Class B) | ASTM A536 (Grade 65-45-12) |
|---|---|
| ISO 185 | ISO 1083 |
| BS 1452 | BS 2789 |
| DIN 1691 | DIN 1693 |
These equivalents ensure that both materials meet international standards for quality and performance.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What are the primary differences between ASTM A126 and ASTM A536?
A1: The main differences lie in their chemical composition and mechanical properties. ASTM A536 offers higher tensile strength, better ductility, and improved impact resistance compared to ASTM A126.
Q2: Can ASTM A126 be used in high-pressure applications?
A2: ASTM A126, particularly Class C, can be used in certain high-pressure applications. However, for more demanding conditions, ASTM A536 is preferred due to its superior strength and durability.
Q3: Is welding possible with ASTM A126 and ASTM A536 materials?
A3: Yes, both materials can be welded. However, welding ASTM A536 requires more specialized procedures due to its higher strength and hardness.
Q4: How does the cost of ASTM A126 compare to ASTM A536?
A4: ASTM A536 is generally more expensive than ASTM A126 due to its enhanced mechanical properties and the additional processing required.
Q5: Are there environmental benefits to using ASTM A536 over ASTM A126?
A5: Yes, ASTM A536 is considered more environmentally friendly due to its longer service life and lower carbon footprint during production.
Q6: Which material is preferred for valve manufacturing?
A6: While both materials are used in valve manufacturing, ASTM A536 is increasingly preferred for its superior mechanical properties, leading to longer-lasting and more reliable valves.
Conclusion
In summary, while ASTM A126 and ASTM A536 are both cast iron standards, they cater to different application requirements. ASTM A126 is suitable for general-purpose applications where cost is a significant factor, whereas ASTM A536 is ideal for demanding applications requiring higher strength, ductility, and impact resistance. Understanding these differences ensures the selection of the appropriate material for specific industrial needs.

