Ductile iron compression sleeves are vital components in various piping systems, providing secure and leak-resistant connections. Proper installation and tightening are crucial to ensure the integrity and longevity of these joints.
1. Understanding Ductile Iron Compression Sleeves
1.1 What Are Ductile Iron Compression Sleeves?
Ductile iron compression sleeves are mechanical fittings designed to join two sections of pipe, typically in water or wastewater systems. They consist of a sleeve that compresses a gasket between the pipe ends, creating a watertight seal. The ductile iron material offers strength and resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for underground and industrial applications.
1.2 Applications of Ductile Iron Compression Sleeves
These sleeves are commonly used in:
-
Water Distribution Systems: Connecting segments of water mains.
-
Sewer Systems: Joining pipes in wastewater infrastructure.
-
Industrial Piping: Facilitating connections in chemical and manufacturing plants.
-
Fire Protection Lines: Ensuring reliable connections in fire suppression systems.
2. Torque Specifications for Ductile Iron Compression Sleeves
2.1 Importance of Proper Torque
Applying the correct torque ensures that the compression sleeve creates a sufficient seal without over-tightening, which could damage the gasket or pipe. Under-tightening may lead to leaks and system failures.
2.2 Recommended Torque Values
According to industry standards, the following torque values are recommended for ductile iron compression sleeves:
| Pipe Size (inches) | Torque (ft-lbs) |
|---|---|
| 6 | 100 |
| 8 | 100 |
| 10 | 100 |
| 12 | 100 |
| 14 | 125 |
| 16 | 125 |
| 18 | 125 |
| 20 | 150 |
Source: JCM Industries Installation Instructions
These values may vary based on specific manufacturer guidelines and the type of gasket used.
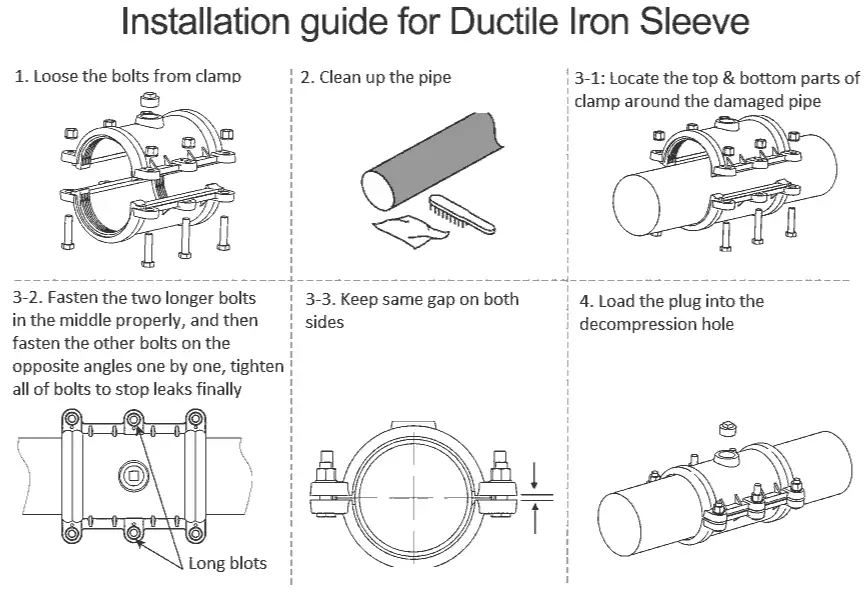
3. Installation Procedures
3.1 Preparing the Pipe Ends
-
Cleanliness: Ensure that the pipe ends are free from debris, rust, or any contaminants.
-
Beveling: If necessary, bevel the pipe ends to facilitate easier insertion into the compression sleeve.
-
Lubrication: Apply a thin layer of lubricant to the gasket to ease installation and prevent damage.
3.2 Assembling the Compression Sleeve
-
Positioning: Slide the compression sleeve over the pipe ends, ensuring that the gasket is properly seated.
-
Aligning: Align the sleeve so that it is centered over the joint.
-
Bolting: Insert and hand-tighten the bolts evenly to hold the sleeve in place.
3.3 Tightening the Bolts
-
Pattern: Use a star or crisscross pattern to tighten the bolts evenly.
-
Torque Application: Using a calibrated torque wrench, tighten the bolts to the recommended torque values.
-
Verification: After tightening, check the sleeve to ensure it is evenly seated and there are no gaps.
4. Maintenance and Inspection
4.1 Regular Inspections
-
Frequency: Conduct visual inspections at regular intervals to check for signs of leakage or wear.
-
Signs to Watch For: Look for water stains, rust, or any deformation of the compression sleeve.
4.2 Re-tightening
-
When Necessary: If leaks are detected, re-tighten the bolts to the specified torque values.
-
Caution: Avoid over-tightening, as this can damage the gasket or pipe.
4.3 Gasket Replacement
-
Timing: Replace gaskets if they show signs of degradation, such as cracking or hardening.
-
Procedure: Remove the old gasket, clean the seating area, and install a new gasket before reassembling the compression sleeve.
5. Troubleshooting Common Issues
5.1 Leaks at the Joint
-
Possible Causes: Under-tightening, damaged gasket, or misalignment.
-
Solutions: Re-tighten bolts, replace the gasket, or realign the sleeve.
5.2 Corrosion
-
Possible Causes: Exposure to corrosive substances or lack of protective coatings.
-
Solutions: Apply appropriate coatings and ensure proper drainage to prevent water accumulation.
5.3 Pipe Movement
-
Possible Causes: Improper restraint or external forces.
-
Solutions: Install pipe restraints and ensure that the system is properly supported.
6. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
6.1 What is the purpose of a compression sleeve in ductile iron piping systems?
A compression sleeve serves to join two sections of ductile iron pipe, creating a secure and leak-resistant connection. It compresses a gasket between the pipe ends, forming a watertight seal.
6.2 How do I determine the correct torque for my compression sleeve?
The correct torque is typically specified by the manufacturer and can vary based on pipe size and gasket type. Refer to the manufacturer’s installation instructions for precise values.
6.3 Can I reuse a compression sleeve after disassembly?
Reusing a compression sleeve is generally not recommended. Gaskets may become deformed or damaged during disassembly, compromising the seal. It’s advisable to use new gaskets and inspect the sleeve for any signs of wear before reuse.
6.4 What tools do I need to install a ductile iron compression sleeve?
Essential tools include a calibrated torque wrench, appropriate wrenches for bolt tightening, and a pipe beveling tool if necessary. Additionally, a lubricant suitable for gaskets can facilitate installation.
6.5 How can I prevent corrosion in ductile iron compression sleeves?
Applying protective coatings, ensuring proper drainage, and conducting regular inspections can help prevent corrosion. In corrosive environments, consider using sleeves with corrosion-resistant coatings or materials.
6.6 What should I do if I detect a leak after installation?
If a leak is detected, first ensure that the system is depressurized. Then, inspect the joint for signs of under-tightening or gasket damage. Re-tighten the bolts to the specified torque or replace the gasket if necessary.
7. Conclusion
Proper installation and maintenance of ductile iron compression sleeves are crucial for the longevity and reliability of piping systems. Adhering to recommended torque specifications, using the correct installation procedures, and conducting regular inspections can prevent common issues and ensure a secure, leak-free connection.
References:
- Ductile Iron Pipe – Wikipedia
- ASTM A536: Standard Specification for Ductile Iron Castings
- JCM Industries Installation Instructions for Ductile Iron Compression Sleeves
- NACE International: Corrosion Protection for Ductile Iron Pipes
- Water Research Foundation: Piping Materials and Joints Best Practices

