Ductile iron pipe (DIP) is a widely used material in water and wastewater infrastructure due to its strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. Understanding the pressure capabilities of ductile iron pipe is crucial for engineers and professionals involved in the design, installation, and maintenance of piping systems. This comprehensive guide delves into the pressure ratings of ductile iron pipe, factors influencing its pressure capacity, and practical considerations for its application.
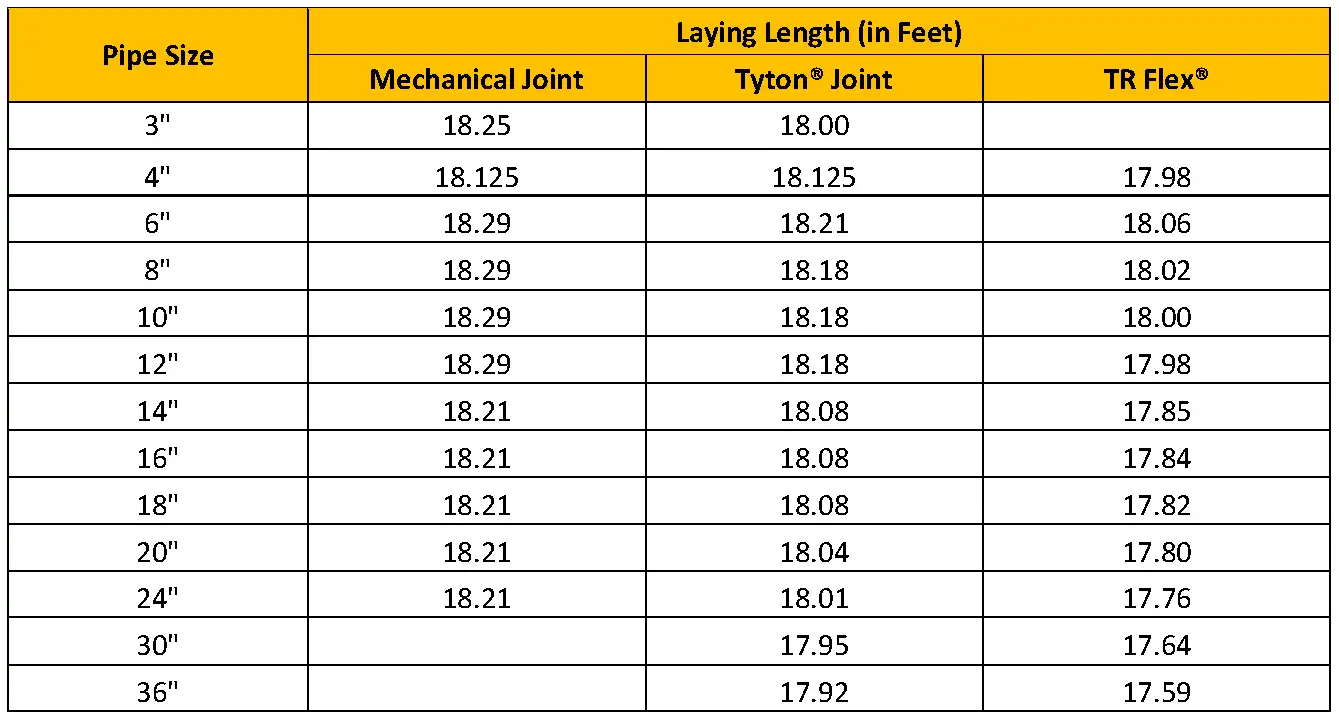
1. Pressure Ratings of Ductile Iron Pipe
1.1 Standard Pressure Classes
Ductile iron pipe is manufactured in various pressure classes, each indicating the maximum allowable internal pressure the pipe can safely handle during operation. These classes are defined by standards such as ANSI/AWWA C150/A21.50 and ANSI/AWWA C151/A21.51. The pressure classes typically range from 150 psi to 350 psi, with some manufacturers offering pipes rated for higher pressures.
| Pressure Class | Nominal Thickness (inches) | Maximum Working Pressure (psi) |
|---|---|---|
| Class 150 | 0.25 | 150 |
| Class 200 | 0.25 | 200 |
| Class 250 | 0.26 | 250 |
| Class 300 | 0.28 | 300 |
| Class 350 | 0.31 | 350 |
Note: The thicknesses provided are nominal values and may vary based on pipe size and manufacturer specifications.
1.2 Surge Allowance and Safety Factor
In addition to the rated working pressure, ductile iron pipes are designed with a surge allowance and a safety factor to account for pressure transients and uncertainties in material properties. According to the AWWA C150 standard, a surge allowance of 100 psi is added to the rated working pressure, and a safety factor of 2.0 is applied to the sum of the working pressure and surge allowance. This ensures that even pipes with lower pressure classes are capable of withstanding higher pressures during transient conditions.
For example, a Class 150 pipe with a rated working pressure of 150 psi would be designed to withstand a maximum internal pressure of 500 psi (150 + 100 surge allowance × 2 safety factor). This conservative design approach enhances the reliability and safety of ductile iron piping systems.
2. Factors Influencing Pressure Capacity
2.1 Pipe Size and Wall Thickness
The pressure capacity of ductile iron pipe is influenced by its size and wall thickness. Larger diameter pipes generally have thicker walls, allowing them to withstand higher internal pressures. Manufacturers provide specifications for each pipe size and pressure class, detailing the corresponding wall thickness and pressure rating.
2.2 Material Strength
Ductile iron possesses superior tensile strength compared to traditional gray iron, enabling it to handle higher internal pressures without failure. The material’s strength is a critical factor in determining the pipe’s pressure capacity.
2.3 Temperature Effects
Temperature can affect the pressure rating of ductile iron pipe. As temperature increases, the material’s strength may decrease, potentially reducing the pipe’s ability to withstand internal pressures. Therefore, it’s essential to consider the operating temperature when evaluating the pressure capacity of ductile iron pipe.
2.4 Joint Type
The type of joint used in ductile iron piping systems can impact the overall pressure rating. For instance, restrained joints provide additional resistance to pressure-induced forces, enhancing the system’s ability to handle higher pressures. Conversely, non-restrained joints may limit the system’s pressure capacity.
3. Applications and Practical Considerations
3.1 Water Distribution Systems
Ductile iron pipe is commonly used in water distribution systems, where pressures typically range from 50 to 150 psi. Class 150 and Class 200 pipes are often sufficient for these applications. However, areas with higher elevation changes or fire protection requirements may necessitate higher pressure classes.
3.2 Wastewater and Sewer Systems
In wastewater and sewer systems, ductile iron pipe is used to convey effluent under varying pressure conditions. The pressure ratings should be selected based on the system’s design parameters, including flow rates and elevation changes.
3.3 Industrial Applications
Industrial applications, such as chemical processing or power generation, may involve higher pressures. In these cases, ductile iron pipe with pressure classes exceeding 350 psi may be required. Manufacturers can provide custom solutions to meet specific pressure requirements.
4. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
4.1 What is the maximum pressure that ductile iron pipe can handle?
The maximum pressure ductile iron pipe can handle depends on factors such as pipe size, wall thickness, material strength, and design specifications. Standard pressure classes range from 150 psi to 350 psi, but pipes are designed with surge allowances and safety factors to withstand higher pressures during transient conditions.
4.2 How does temperature affect the pressure rating of ductile iron pipe?
As temperature increases, the tensile strength of ductile iron may decrease, potentially reducing the pipe’s ability to withstand internal pressures. It’s essential to consider the operating temperature when evaluating the pressure capacity of ductile iron pipe and to consult manufacturer specifications for temperature-related adjustments.
4.3 Can ductile iron pipe be used for high-pressure applications?
Yes, ductile iron pipe can be used for high-pressure applications. Manufacturers offer pipes with pressure classes exceeding 350 psi for specialized applications. It’s crucial to select the appropriate pressure class based on the system’s design requirements and to consult with manufacturers for custom solutions.
4.4 What factors should be considered when selecting the pressure class of ductile iron pipe?
When selecting the pressure class of ductile iron pipe, consider factors such as the system’s operating pressure, temperature conditions, pipe size, wall thickness, joint type, and potential surge pressures. Consulting with engineers and manufacturers can help determine the appropriate pressure class for specific applications.
4.5 How is the pressure rating of ductile iron pipe determined?
The pressure rating of ductile iron pipe is determined through calculations based on factors such as the pipe’s dimensions, material strength, and design specifications. Standards like ANSI/AWWA C150/A21.50 provide guidelines for determining the pressure rating, including considerations for surge allowances and safety factors.
Conclusion
Ductile iron pipe is a robust and reliable material for various piping applications, offering impressive pressure handling capabilities. Understanding the factors that influence its pressure capacity, including pipe size, material strength, temperature effects, and joint type, is essential for ensuring the safety and efficiency of piping systems. By carefully selecting the appropriate pressure class and considering all relevant factors, engineers and professionals can design and maintain piping systems that meet the demands of their specific applications.
References:
- AWWA C150 – Standard for the Design and Installation of Ductile-Iron Pipe
- ASTM A536 – Standard Specification for Ductile Iron Castings
- ISO 2531 – Ductile Iron Pipes for Water and Sewage
- ANSI Standards – Pressure Ratings and Design for Ductile Iron Pipe
- EPA – Safe Drinking Water Act and Standards for Water Systems
