When comparing the price of cast iron versus ductile iron, cast iron generally appears less expensive on a per-ton or per-kilogram basis. However, when evaluated in terms of long-term performance, mechanical advantages, reduced maintenance, and overall lifecycle cost, ductile iron provides better value for most structural, automotive, and pipeline applications. This article provides a comprehensive comparison of cast iron and ductile iron prices, explains the influencing cost factors, and helps buyers, engineers, and procurement managers make informed material choices in 2025.
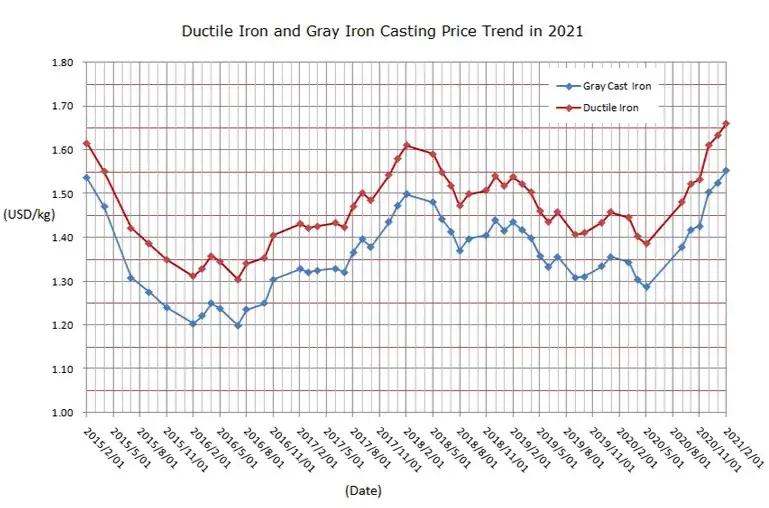
1. Overview of Cast Iron and Ductile Iron
Cast iron and ductile iron are both ferrous materials, but their composition and mechanical characteristics are different. Cast iron contains flake graphite, which gives it brittleness, while ductile iron features spheroidal graphite, offering higher ductility and strength. These metallurgical differences influence their market prices, applications, and processing methods.
Table: Basic Properties Comparison
| Property | Cast Iron | Ductile Iron |
|---|---|---|
| Graphite Structure | Flake | Nodular (spheroidal) |
| Tensile Strength | ~200 MPa | ~500 MPa |
| Elongation | <1% | 10–18% |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | Better with coatings |
| Typical Applications | Cookware, Engine Blocks | Pipes, Automotive Parts |
| Material Cost (2025) | $450–$600/ton | $600–$800/ton |
Ductile iron typically costs 20–30% more due to added alloying elements (like magnesium), refining processes, and demand in infrastructure projects.
2. Cost Comparison by Application
A. Water Infrastructure
In the waterworks industry, ductile iron pipes are preferred over cast iron due to their strength and flexibility. Although they are costlier upfront, the reduction in failure risk makes them more economical over time.
B. Automotive Industry
Cast iron is used in components where rigidity is needed, but ductile iron is selected for parts requiring high fatigue resistance. The cost-benefit analysis often favors ductile iron despite higher material costs.
C. Construction & Machinery
When evaluating material costs in construction machinery, ductile iron’s strength-to-weight ratio reduces component mass, enabling cost savings on fuel and operational efficiency.
Table: Estimated Price Per Kilogram in Key Industries (2025)
| Industry | Cast Iron (USD/kg) | Ductile Iron (USD/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| Water Infrastructure | 0.55 | 0.78 |
| Automotive | 0.50 | 0.72 |
| Machinery & Tools | 0.48 | 0.70 |
3. Factors Affecting the Price of Cast Iron and Ductile Iron
Several market and manufacturing-related factors influence the price of cast iron and ductile iron:
A. Raw Material Costs
-
Iron ore and scrap iron prices
-
Alloying elements like magnesium (for ductile iron)
-
Foundry coke or electric furnace costs
B. Energy and Labor Costs
Energy-intensive casting processes affect both materials but more so for ductile iron due to additional nodularization.
C. Supply and Demand
Urbanization and global infrastructure projects have increased demand for ductile iron pipes, raising its price globally.
D. Processing Complexity
-
Ductile iron requires inoculation and controlled cooling
-
Quality assurance adds to manufacturing costs
Table: Cost Contribution by Factor
| Cost Factor | Cast Iron (%) | Ductile Iron (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | 45 | 50 |
| Energy & Utilities | 20 | 25 |
| Labor | 10 | 10 |
| Processing & QA | 15 | 10 |
| Overheads & Margin | 10 | 5 |
4. Regional Price Trends and Global Market Analysis (2024–2025)
Prices for both materials vary widely depending on location, regulations, labor rates, and import/export tariffs.
A. North America
-
Ductile iron prices in the US are relatively stable but rising due to EPA-compliant manufacturing standards.
B. Europe
-
EU green manufacturing regulations affect costs for ductile iron, making it more expensive than in Asia.
C. Asia-Pacific
-
China remains the largest producer and exporter of both cast and ductile iron.
-
Prices are lower due to scale and lower labor costs.
Table: 2025 Regional Price Comparison (USD/ton)
| Region | Cast Iron Price | Ductile Iron Price |
|---|---|---|
| USA | $600 | $800 |
| Germany | $620 | $850 |
| China | $450 | $630 |
| India | $470 | $650 |
5. Lifecycle Cost and Total Cost of Ownership
While ductile iron has a higher initial price, its lifecycle cost often makes it more economical in the long run.
Lifecycle Cost Factors
-
Installation costs
-
Maintenance and repair frequency
-
Expected lifespan
-
Failure risk and downtime cost
Ductile iron often requires fewer repairs and has a 100-year lifespan in pipelines compared to 50 years for cast iron.
Table: 50-Year Cost Comparison
| Parameter | Cast Iron ($) | Ductile Iron ($) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Material Cost | 100,000 | 130,000 |
| Installation Cost | 40,000 | 45,000 |
| Maintenance (50 yrs) | 80,000 | 30,000 |
| Replacement Cost | 60,000 | 0 |
| Total | 280,000 | 205,000 |
6. Environmental and Sustainability Impacts on Pricing
Sustainability is a growing factor in purchasing decisions. Ductile iron, despite being more energy-intensive to produce, often results in lower emissions across the lifecycle.
Environmental Considerations
-
Cast iron has higher failure rates, leading to more replacements and waste.
-
Ductile iron’s recyclability and durability make it a preferred green building material.
Certifications like ISO 14001 and LEED prefer ductile iron in infrastructure projects.
Sustainable Manufacturing Trends
-
Use of recycled scrap
-
Electric arc furnace usage
-
Waste heat recovery systems in foundries
Table: Sustainability Score Comparison
| Factor | Cast Iron | Ductile Iron |
|---|---|---|
| Recyclability | High | High |
| Manufacturing Emissions | Lower | Slightly Higher |
| Durability | Moderate | Excellent |
| Failure Rate (50 yrs) | High | Low |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why is ductile iron more expensive than cast iron?
Ductile iron is more expensive due to its specialized production process, which involves the addition of magnesium and precise temperature control to create a nodular graphite structure. This enhances its strength, ductility, and resistance to impact, making it ideal for high-performance applications. Additionally, ductile iron often includes higher quality assurance steps and meets stricter international standards, contributing to its higher market price.
2. Is it worth paying more for ductile iron?
Yes, in many scenarios ductile iron offers a better return on investment. Despite the higher upfront cost, its extended lifespan, lower failure rate, and reduced maintenance costs make it more economical over the long term. For example, in municipal water systems, ductile iron pipes are preferred for their ability to withstand pressure and ground movement without cracking.
3. What are the main applications that justify ductile iron’s higher price?
Ductile iron is commonly used in pressure pipes, automotive components, and heavy-duty machinery where strength and fatigue resistance are critical. Its ability to withstand high loads and dynamic stress makes it preferable in high-risk or safety-critical installations, such as bridges, sewer lines, and hydraulic components.
4. Can cast iron be replaced with ductile iron in old systems?
Yes, ductile iron is often used as a modern replacement for cast iron in retrofitting and pipeline rehabilitation projects. It can handle higher internal pressures and external stress, making it suitable for replacing aging infrastructure. However, due to differences in mechanical properties, fittings and joints may require modification.
5. How do global supply chains affect the prices of cast and ductile iron?
Supply chain disruptions, such as those caused by pandemics or geopolitical tensions, can affect the availability and price of both materials. Ductile iron is especially sensitive to magnesium supply and energy prices. Cast iron, being simpler and more common, tends to be less volatile in price.
6. Which is better for outdoor use: cast iron or ductile iron?
Ductile iron is generally better suited for outdoor use due to its superior impact resistance and flexibility. When combined with proper coatings (such as zinc or bitumen), ductile iron offers long-term protection against environmental stressors, including moisture, UV exposure, and chemical corrosion.
References:
1. Ductile Iron Pipe Research Association (DIPRA) – Why Use Ductile Iron Pipe?
2.ISO 2531:2021 – Ductile Iron Pipes, Fittings, Accessories and Their Joints for Water Applications
4. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) – Clean Water Infrastructure Sustainability Policy
