When it comes to controlling the flow of liquids and gases through pipelines, the choice of valve is critical. Valves are integral components in many systems, from industrial applications to residential plumbing. Three of the most commonly used valve types are the butterfly valve, gate valve, and ball valve. Each of these valves has distinct advantages, features, and applications. Understanding the differences between them can help you make an informed decision on which valve is best suited for your specific needs.
In this article, we will provide an in-depth comparison of the butterfly valve, gate valve, and ball valve, covering their functionality, design, pros, cons, applications, and more.
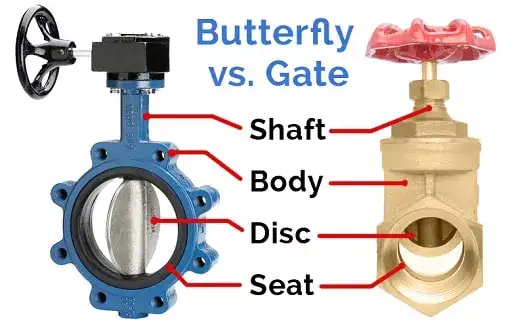
1. What is a Butterfly Valve?
A butterfly valve is a flow control device used to regulate the flow of liquids, gases, and slurry through a pipeline. It consists of a circular disc or vane that rotates around a shaft to open or close the flow passage. The valve’s operation is simple, and it is known for its lightweight and compact design, making it ideal for applications where space is limited.
Butterfly valves are commonly used in industries such as water treatment, food and beverage, HVAC systems, and chemical processing. They are available in various types, including wafer, lug, and double-flanged models, offering versatility for different installation needs.
Features of Butterfly Valves:
-
Compact design: Ideal for tight spaces.
-
Quick operation: Open and close quickly.
-
Cost-effective: Typically less expensive than other valve types.
-
Variety of materials: Available in various materials, including cast iron, stainless steel, and plastic.
2. What is a Gate Valve?
A gate valve is a linear motion valve used to start or stop the flow of a fluid. It features a gate or wedge-shaped disc that slides between two seats to control the flow of the medium. The gate valve is typically used in applications where the valve either remains fully open or fully closed, as it is not designed for flow regulation.
Gate valves are often used in large diameter pipes, where space is not a concern, and where a tight shutoff is required. They are common in water, oil, and gas distribution systems.
Features of Gate Valves:
-
Tight seal: Provides a tight shutoff when fully closed.
-
Simple operation: Works with a simple rising or non-rising stem.
-
Large size: Suitable for large pipelines and high-pressure applications.
-
Not ideal for throttling: They are not designed for precise flow control.
3. What is a Ball Valve?
A ball valve is a quarter-turn valve that uses a spherical ball with a hole or port in the center to control the flow of fluid. When the valve handle is turned, the ball rotates, allowing or blocking the flow of the medium. Ball valves are known for their durability, reliability, and ability to provide quick and precise shutoff.
Ball valves are commonly used in both residential and industrial applications, including plumbing systems, HVAC, chemical processing, and oil and gas operations. They are available in a variety of materials, such as brass, stainless steel, and PVC, depending on the application.
Features of Ball Valves:
-
Quick shutoff: Provides fast and reliable shutoff.
-
Compact design: Suitable for smaller pipelines.
-
Reliable: Offers durability and long service life.
-
Excellent for throttling: Some ball valves are designed for precise flow control.
4. Design and Operation: How They Work
Understanding how each valve works can help you assess which is most suitable for your application. Let’s break down the mechanisms of each valve:
Butterfly Valve Operation:
A butterfly valve consists of a round disc mounted on a shaft. When the valve is turned, the disc rotates 90 degrees, either opening or closing the flow path. The valve’s design allows for quick operation, and it is often used in situations where space is limited and a full shutoff is not always required. Butterfly valves typically have a lower pressure drop, which makes them energy-efficient.
Gate Valve Operation:
Gate valves operate by raising and lowering a gate or wedge between two seats, which stops or starts the flow of fluid. Gate valves are most commonly used for fully open or fully closed applications. The gate rises when the valve is open, allowing the fluid to flow through. Gate valves are slower to operate compared to butterfly and ball valves, and their operation requires more space.
Ball Valve Operation:
Ball valves work by rotating a ball with a hole or port in the center. The ball turns a quarter-turn (90 degrees), and when the port aligns with the pipeline, fluid flows through. When the ball is rotated 90 degrees in the opposite direction, the port is closed, blocking the flow. Ball valves are known for their ease of operation and tight sealing capabilities.
5. Comparison of Butterfly Valve vs Gate Valve vs Ball Valve
Here is a comparison of the three valve types based on several important criteria:
| Criteria | Butterfly Valve | Gate Valve | Ball Valve |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operation | 90-degree rotation, quick actuation | Linear motion, gate slides in/out | 90-degree rotation, quick actuation |
| Seal Type | Partial seal, ideal for throttling | Full seal, best for full closure | Full seal, best for full closure |
| Flow Regulation | Good for flow regulation | Not suitable for flow regulation | Good for flow regulation (with some models) |
| Space Requirements | Compact and lightweight | Larger size, requires more space | Compact design, suitable for smaller systems |
| Cost | Low-cost option | Higher cost, especially for larger sizes | Medium to high cost, depending on material and design |
| Durability | Moderate, depends on material | Very durable, especially in larger systems | Highly durable, long-lasting under pressure |
| Common Applications | HVAC, water treatment, chemical systems | Water distribution, oil and gas | Plumbing, industrial, chemical systems |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, easy to service | Moderate maintenance, can become jammed | Low maintenance, easy to replace parts |
6. Applications of Each Valve Type
Each of these valves excels in different applications:
-
Butterfly Valve Applications:
-
HVAC systems
-
Water treatment facilities
-
Food and beverage industries
-
Chemical processing plants
-
Fire protection systems
-
-
Gate Valve Applications:
-
Water distribution systems
-
Wastewater treatment
-
Oil and gas pipelines
-
High-pressure systems requiring full shutoff
-
-
Ball Valve Applications:
-
Residential plumbing
-
Oil and gas industry
-
Chemical and petrochemical processing
-
HVAC systems
-
Water treatment facilities
-
7. Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Valve
Butterfly Valve Advantages:
-
Compact and lightweight
-
Quick actuation, ideal for throttling
-
Cost-effective
-
Low pressure drop, energy-efficient
Butterfly Valve Disadvantages:
-
Not ideal for high-pressure applications
-
May not provide a tight shutoff in certain conditions
-
Limited durability under extreme temperatures
Gate Valve Advantages:
-
Provides a tight seal for full shutoff
-
Durable and reliable
-
Suitable for large pipeline systems
Gate Valve Disadvantages:
-
Slow operation, not ideal for quick flow control
-
High maintenance in some cases
-
Large and heavy, requiring more space
Ball Valve Advantages:
-
Quick and reliable shutoff
-
High durability and resistance to wear
-
Excellent for controlling flow in industrial applications
Ball Valve Disadvantages:
-
Higher initial cost compared to butterfly valves
-
May not be suitable for throttling in some models
-
Requires careful installation to avoid leakage
8. Factors to Consider When Choosing a Valve
When choosing between a butterfly valve, gate valve, and ball valve, consider the following factors:
-
Application Type: Consider the environment and purpose. For throttling and regulating flow, butterfly valves are ideal. For tight shutoff and high-pressure systems, gate valves and ball valves are better choices.
-
Size and Space: Butterfly valves are great for tight spaces, while gate valves require more room for installation. Ball valves offer a good balance between space-saving and functionality.
-
Cost: Butterfly valves are typically the most cost-effective, but for high-end applications, ball valves may offer greater longevity.
-
Maintenance Requirements: Ball and butterfly valves generally require less maintenance compared to gate valves, which can be prone to wear and tear.
9. Cost Comparison: Butterfly, Gate, and Ball Valves
The cost of each valve type varies based on material, size, and application. Here’s a general price range:
| Valve Type | Price Range |
|---|---|
| Butterfly Valve | $50 to $1,000+ depending on size and material |
| Gate Valve | $150 to $3,000+ depending on size and pressure rating |
| Ball Valve | $100 to $2,500+ depending on size and material |
10. FAQs
Q1: Which valve is best for high-pressure systems?
For high-pressure applications, gate valves and ball valves are typically preferred due to their robust sealing capabilities. Butterfly valves may not be suitable for extreme pressure conditions.
Q2: Can a butterfly valve be used for throttling?
Yes, butterfly valves are often used for throttling applications due to their ability to regulate flow effectively. However, they are best suited for lower-pressure systems.
Q3: What is the difference between a full port and a standard port ball valve?
A full-port ball valve has a larger opening that matches the size of the pipe, allowing for minimal pressure drop, while a standard-port ball valve has a smaller opening, resulting in higher pressure loss.
Q4: Are gate valves suitable for regulating flow?
Gate valves are not designed for flow regulation. They are intended for fully open or fully closed applications and are best used in situations where you need a tight shutoff.
Q5: How long do ball valves last?
Ball valves are highly durable and can last for decades when properly maintained. They are resistant to wear and tear and are ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
Q6: What are the most common materials used for valves?
Common materials for valves include cast iron, stainless steel, brass, and PVC. The choice of material depends on the application, fluid type, and pressure conditions.
Conclusion
Choosing the right valve for your system depends on your specific needs, including the type of fluid being controlled, system pressure, size constraints, and budget. Butterfly valves are ideal for lightweight and compact applications, gate valves are suited for tight shutoff and high-pressure systems, and ball valves offer reliable performance with quick actuation for a wide range of applications.
