The ASTM A536 D4512 ductile iron equivalent refers to high-strength nodular iron grades meeting 65-45-12 (ASTM) or EN-GJS-400-15/500-7 (ISO) specifications, widely used in valves, pipe fittings, and automotive components.
1. Understanding D4512 Ductile Iron
1.1 Definition and Classification
D4512 is a designation under the SAE J434 standard, representing a specific grade of ductile iron. Ductile iron is characterized by its nodular graphite inclusions, which impart enhanced ductility and toughness compared to traditional gray cast iron. The “D” in D4512 denotes ductile iron, while “4512” indicates the material’s minimum tensile strength and elongation percentage.
1.2 Chemical Composition
The typical chemical composition of D4512 ductile iron is as follows:
| Element | Minimum (%) | Maximum (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 3.4 | 3.8 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| Silicon (Si) | 2.2 | 2.75 |
| Chromium (Cr) | – | 0.08 |
| Nickel (Ni) | – | 0.5 |
| Copper (Cu) | – | 0.4 |
| Magnesium (Mg) | 0.025 | 0.055 |
These elements contribute to the material’s mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and overall performance.
1.3 Microstructure
D4512 ductile iron typically exhibits a ferritic-pearlitic microstructure. The ferritic matrix provides good ductility and impact resistance, while the pearlitic regions enhance strength and wear resistance. The balance between these phases can be adjusted through heat treatment and alloying to meet specific application requirements.
2. Mechanical Properties of D4512
Understanding the mechanical properties of D4512 is essential for determining its suitability for various applications.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (UTS) | 65,000 psi (450 MPa) |
| Yield Strength (YS) | 45,000 psi (310 MPa) |
| Elongation | 12% |
| Hardness (Brinell) | 170-230 HB |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 24 x 10^6 psi (165 GPa) |
| Density | 0.256 lb/in³ (7.1 g/cm³) |
These properties make D4512 suitable for components requiring a combination of strength, ductility, and wear resistance.
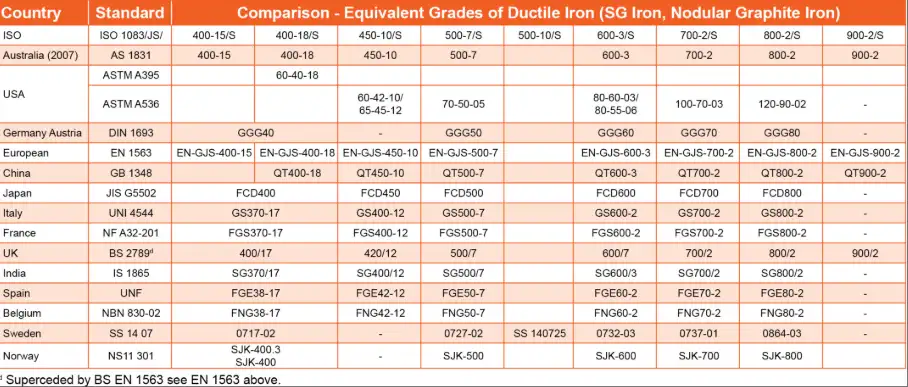
3. Global Equivalents of D4512
D4512 ductile iron has equivalents in various international standards, facilitating its use in global applications.
| Standard | Grade | Country/Region |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM A536 | 65-45-12 | USA |
| ISO 1083 | 450-10 | International |
| EN 1563 | EN-GJS-450-10 | Europe |
| DIN 1693 | GGG 40 | Germany |
| JIS G5502 | FCD450 | Japan |
| GB/T 1348 | QT450-10 | China |
| BS 2789 | 420/12 | United Kingdom |
| UNI 4544 | GS 450-10 | Italy |
These equivalents ensure compatibility and standardization across different regions, simplifying material selection and procurement processes.
4. Applications of D4512 Ductile Iron
D4512 ductile iron is utilized in various industries due to its favorable mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness.
4.1 Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, D4512 is used for components such as:
-
Engine blocks
-
Crankshafts
-
Suspension parts
-
Brake components
Its strength and fatigue resistance make it ideal for parts subjected to dynamic loads.
4.2 Machinery and Equipment
D4512 is employed in manufacturing machinery and equipment components, including:
-
Gearboxes
-
Pumps
-
Valves
-
Hydraulic cylinders
Its machinability and wear resistance contribute to the longevity and reliability of these components.
4.3 Construction and Infrastructure
In construction, D4512 is used for:
-
Manhole covers
-
Pipe fittings
-
Structural supports
Its durability and load-bearing capacity are essential for infrastructure applications.
5. Comparison with Other Ductile Iron Grades
Understanding how D4512 compares to other ductile iron grades aids in selecting the appropriate material for specific applications.
| Grade | Tensile Strength (psi) | Yield Strength (psi) | Elongation (%) | Hardness (HB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D4018 | 60,000 | 40,000 | 18 | 130-180 |
| D4512 | 65,000 | 45,000 | 12 | 170-230 |
| D5006 | 70,000 | 50,000 | 10 | 200-250 |
| D5504 | 80,000 | 55,000 | 6 | 230-300 |
D4512 offers a balanced combination of strength and ductility, making it versatile for various applications.
6. Heat Treatment and Machinability
6.1 Heat Treatment
D4512 can undergo heat treatments to modify its microstructure and mechanical properties:
-
Annealing: Reduces hardness and improves ductility.
-
Normalizing: Enhances strength and toughness.
-
Quenching and Tempering: Increases hardness and wear resistance.
The choice of heat treatment depends on the desired balance between strength, hardness, and ductility.
6.2 Machinability
D4512 exhibits good machinability due to its ferritic-pearlitic microstructure. The presence of graphite nodules acts as a lubricant during machining, reducing tool wear and improving surface finish. However, tool selection and cutting parameters should be optimized to achieve the best results.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the significance of the “65-45-12” designation in ASTM A536?
A1: The “65-45-12” designation in ASTM A536 refers to the minimum mechanical properties of the ductile iron grade. Specifically, it indicates a minimum tensile strength of 65,000 psi, a minimum yield strength of 45,000 psi, and a minimum elongation of 12%. These values provide a quick reference to the material’s strength and ductility, aiding engineers and designers in material selection for various applications.
Q2: How does D4512 compare to gray cast iron in terms of mechanical properties?
A2: D4512 ductile iron offers superior mechanical properties compared to gray cast iron. While gray cast iron has excellent compressive strength and damping capacity, it is brittle and lacks tensile strength and ductility. In contrast, D4512 exhibits higher tensile and yield strengths, along with improved elongation and impact resistance. This makes D4512 more suitable for components subjected to dynamic loads and requiring toughness.
Q3: Can D4512 ductile iron be welded?
A3: Welding D4512 ductile iron is possible but requires careful consideration. The material’s graphite nodules can lead to challenges such as porosity and reduced weld strength. Preheating the material, using appropriate filler materials, and post-weld heat treatment can mitigate these issues. However, welding should be approached cautiously, and alternative joining methods like mechanical fastening or adhesive bonding may be preferred when feasible.
References:
- ASTM A536 Standard Specification for Ductile Iron Castings – ASTM International official website providing the detailed specifications and mechanical property requirements for ductile iron grades including 65-45-12.
- Ductile Iron – Wikipedia – Comprehensive overview of ductile iron properties, microstructure, heat treatment, and applications, serving as an authoritative general reference.
- ISO 1083: Cast irons — Classification – International Organization for Standardization’s classification for ductile iron grades equivalent to ASTM A536 standards.
- SAE J434 – Ductile Iron Casting Grades – SAE International document detailing classification and properties of ductile iron grades including D4512.
- How to Weld Ductile Iron – TWI Global – Trusted industry guidance on welding challenges and procedures specific to ductile iron materials like D4512.
