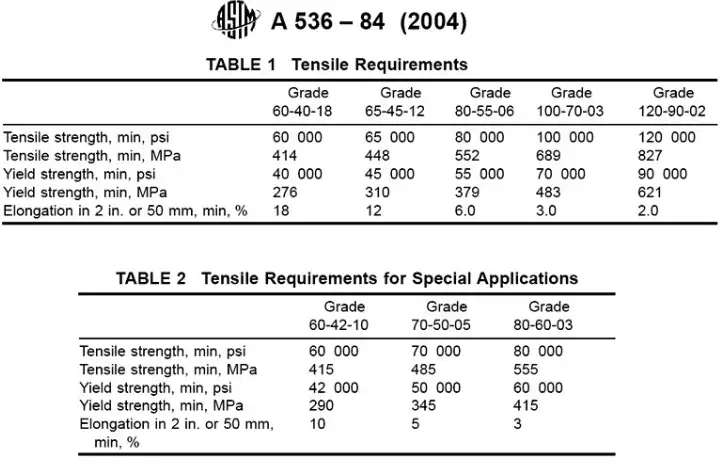
ASTM A536 100-70-03 ductile iron is a high-strength material known for its excellent mechanical properties, including a minimum tensile strength of 100,000 psi, yield strength of 70,000 psi, and 3% elongation. Its pearlitic microstructure provides a balance of strength and wear resistance, making it suitable for demanding applications in automotive, fluid power, and heavy machinery industries.
1. Mechanical Properties of 100-70-03 Ductile Iron
The mechanical properties of ASTM A536 100-70-03 ductile iron are as follows:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | ≥ 100,000 psi |
| Yield Strength | ≥ 70,000 psi |
| Elongation | ≥ 3% |
| Brinell Hardness (BHN) | 240–300 |
| Density | 0.257–0.26 lb/in³ |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.06 cal/cm·sec·°C |
| Specific Heat | 0.15 Btu/lb·°F |
| Melting Temperature | ~2100°F |
These properties make 100-70-03 ductile iron ideal for components requiring high strength and moderate ductility.
2. Chemical Composition and Microstructure
The typical chemical composition of 100-70-03 ductile iron is:
| Element | Minimum (%) | Maximum (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon | 3.4 | 3.8 |
| Silicon | 1.8 | 2.8 |
| Manganese | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| Chromium | 0.0 | 0.08 |
| Nickel | 0.0 | 1.5 |
| Copper | 0.15 | 1.2 |
| Magnesium | 0.025 | 0.06 |
The microstructure consists of graphite spheroids in a pearlitic matrix, providing a combination of strength and wear resistance.
3. Heat Treatment and Processing
Heat treatment enhances the mechanical properties and dimensional stability of 100-70-03 ductile iron. Common heat treatments include:
-
Normalizing: Refines grain structure and improves mechanical properties.
-
Tempering: Reduces brittleness and enhances toughness.
-
Quenching and Tempering: Increases strength and hardness.
Proper heat treatment ensures the material meets the desired specifications for various applications.
4. Applications in Various Industries
100-70-03 ductile iron is utilized in numerous industries due to its strength and durability:
-
Automotive: Gears, crankshafts, and suspension components.
-
Fluid Power: Cylinder blocks, manifolds, and pistons.
-
Machinery: Flywheels, pulleys, and housings.
-
Pump and Compressor: Housings, rotors, and liners.
Its versatility makes it a preferred material for components subjected to high stress and wear.
5. Comparative Analysis with Other Ductile Iron Grades
Comparing 100-70-03 with other ductile iron grades:
| Grade | Tensile Strength (psi) | Yield Strength (psi) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 60-40-18 | 60,000 | 40,000 | 18 |
| 65-45-12 | 65,000 | 45,000 | 12 |
| 80-55-06 | 80,000 | 55,000 | 6 |
| 100-70-03 | 100,000 | 70,000 | 3 |
100-70-03 offers higher strength but lower ductility compared to lower grades, making it suitable for applications where strength is critical.
6. Standards and Specifications
100-70-03 ductile iron conforms to various international standards:
| Standard | Equivalent Grade |
|---|---|
| ASTM | A536 100-70-03 |
| SAE | D7003 |
| ISO | 700-2 |
| EN | GJS-700-2 |
| DIN | GGG70 |
These standards ensure consistency in mechanical properties and chemical composition across different manufacturers and regions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What are the key mechanical properties of 100-70-03 ductile iron?
A1: 100-70-03 ductile iron has a minimum tensile strength of 100,000 psi, yield strength of 70,000 psi, and elongation of at least 3%. Its Brinell hardness ranges from 240 to 300, making it suitable for high-strength applications.
Q2: How does the chemical composition affect the properties of 100-70-03 ductile iron?
A2: The chemical composition, particularly the carbon and silicon content, influences the formation of graphite spheroids and the pearlitic matrix, which in turn affect the strength, hardness, and ductility of the material.
Q3: What heat treatments are commonly applied to 100-70-03 ductile iron?
A3: Common heat treatments include normalizing, tempering, and quenching and tempering. These processes enhance mechanical properties and ensure dimensional stability for various applications.
Q4: In which industries is 100-70-03 ductile iron commonly used?
A4: It is widely used in automotive, fluid power, machinery, and pump and compressor industries for components like gears, pistons, housings, and rotors due to its high strength and wear resistance.
Q5: How does 100-70-03 compare to other ductile iron grades?
A5: Compared to lower grades like 60-40-18 or 65-45-12, 100-70-03 offers higher tensile and yield strength but lower elongation, making it more suitable for high-stress applications where ductility is less critical.
Q6: What standards govern the specifications of 100-70-03 ductile iron?
A6: It conforms to standards such as ASTM A536 100-70-03, SAE D7003, ISO 700-2, EN GJS-700-2, and DIN GGG70, ensuring consistent quality and properties across different manufacturers and regions.
References:
ASTM A536 – Standard Specification for Ductile Iron Castings — ASTM International
SAE J1398 – Ductile Iron Grades and Properties — SAE International
