في عالم مواد الحديد الزهر، ASTM A126 و ASTM A536 هما معياران بارزان يلبيان الاحتياجات الصناعية المختلفة. في حين أن كلاهما يندرجان تحت فئة الحديد الزهر، إلا أنهما يتمتعان بخصائص مميزة تجعلهما مناسبين لتطبيقات محددة. يعد فهم الاختلافات بين هذين المعيارين أمرًا بالغ الأهمية للمهندسين والمصنعين والمتخصصين في المشتريات لاختيار المواد المناسبة لمشاريعهم.
1. نظرة عامة على ASTM A126
ASTM A126 هي مواصفات قياسية لمسبوكات الحديد الرمادي المستخدمة في التطبيقات الميكانيكية وتطبيقات الضغط. يتم تصنيفها في المقام الأول إلى ثلاث فئات:
-
الفئة أ: مخصص للاستخدام في البخار والتطبيقات الأخرى ذات درجات الحرارة العالية.
-
الفئة ب: مصممة لتطبيقات الأغراض العامة.
-
الفئة C: تُستخدم للتطبيقات التي تتطلب قوة أعلى.
وتتميز هذه المسبوكات ببنية الجرافيت المجهرية المتقشرة التي توفر قابلية تشغيل آلي ممتازة وخصائص تخميد ممتازة.
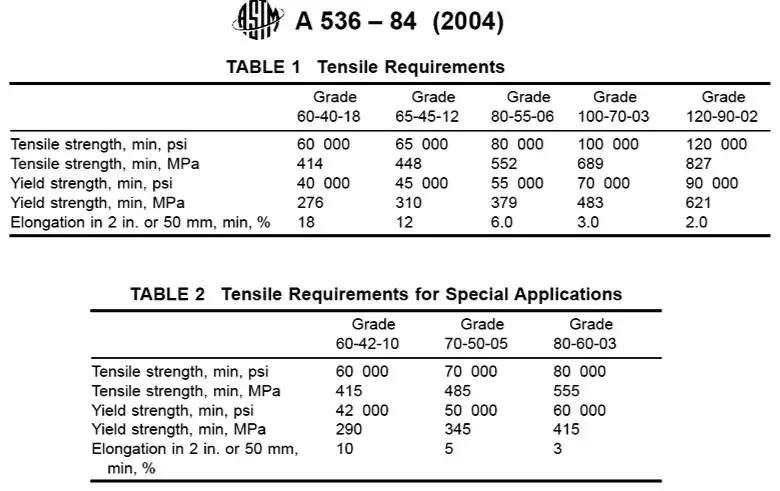
2. نظرة عامة على ASTM A536
ASTM A536 هي المواصفة القياسية لمسبوكات حديد الدكتايل والمعروفة أيضًا باسم حديد الزهر العقدي. يتم إنتاج هذه المادة عن طريق إضافة كمية صغيرة من المغنيسيوم إلى الحديد المصهور، مما ينتج عنه بنية مجهرية من عقيدات الجرافيت الكروية. تشمل الدرجات الأساسية بموجب هذا المعيار ما يلي:
-
الصف 60-40-18: يوفر توازناً بين القوة والليونة.
-
الصف 65-45-12: يوفر قوة أعلى وليونة معتدلة.
-
الصف 80-55-06: يوفر قوة فائقة واستطالة أقل.
يُعرف حديد الدكتايل بخصائصه الميكانيكية المحسّنة مقارنةً بالحديد الرمادي، بما في ذلك قوة الشد الأعلى ومقاومة الصدمات.
3. مقارنة التركيب الكيميائي
| العنصر | ASTM A126 (الفئة ب) | ASTM A536 (الدرجة 65-45-12) |
|---|---|---|
| الكربون | 3.0% – 3.4% | 3.4% – 3.8% |
| السيليكون | 1.8% – 2.8% | 2.5% – 3.0% |
| المنجنيز | 0.6% – 1.0% | 0.15% – 0.35% |
| الكبريت | ≤0.10% | ≤0.0.020% |
| الفوسفور | ≤0.08% | ≤0.060% |
يسلط هذا الجدول الضوء على الاختلافات في التركيب الكيميائي بين المواصفتين القياسيتين، مما يؤثر على خصائص كل منهما ومدى ملاءمتها للاستخدامات المختلفة.
4. مقارنة الخواص الميكانيكية
| الممتلكات | ASTM A126 (الفئة ب) | ASTM A536 (الدرجة 65-45-12) |
|---|---|---|
| قوة الشد | 30,000 - 60,000 رطل لكل بوصة مربعة | ≥65,000 رطل لكل بوصة مربعة |
| قوة المردود | غير محدد | ≥45,000 رطل لكل بوصة مربعة |
| الاستطالة | 1.5% – 3.0% | ≥12% |
| الصلابة | 170 - 220 HB 170 - 220 HB | 131 - 220 هكتار |
| مقاومة الصدمات | منخفضة | عالية |
تتفوق الخواص الميكانيكية للمواصفة ASTM A536 بشكل عام على المواصفة ASTM A126، حيث توفر قوة أعلى وليونة أفضل.
5. اختلافات البنية المجهرية
-
ASTM A126: يتميز ببنية جرافيت متقشرة، والتي توفر قدرة ممتازة على التخميد ولكن قوة شد ومقاومة أقل للصدمات.
-
ASTM A536: يُظهر هيكل الجرافيت الكروي، مما يؤدي إلى تحسين قوة الشد والليونة ومقاومة الصدمات.
تؤثر هذه الاختلافات في البنية المجهرية بشكل كبير على خصائص أداء المواد.
6. التطبيقات والاستخدامات الصناعية
| مجال التطبيق | ASTM A126 (الفئة ب) | ASTM A536 (الدرجة 65-45-12) |
|---|---|---|
| أجسام الصمامات وغطاء المحرك | نعم | نعم |
| مكونات المضخة | نعم | نعم |
| قطع غيار السيارات | لا يوجد | نعم |
| المكونات الهيكلية | لا يوجد | نعم |
| الآلات الثقيلة | لا يوجد | نعم |
وعلى الرغم من استخدام كلتا المادتين في أجسام الصمامات وأغطية الصمامات، إلا أن ASTM A536 أكثر انتشارًا في التطبيقات التي تتطلب قوة ومقاومة أعلى للصدمات.
7. اعتبارات التكلفة
وبصفة عامة، تكون مواد ASTM A536 أغلى من ASTM A126 بسبب خواصها الميكانيكية الفائقة والمعالجة الإضافية المطلوبة. ومع ذلك، يمكن أن يؤدي الأداء المحسّن إلى توفير في التكاليف في التطبيقات التي تكون فيها المتانة والموثوقية أمرًا بالغ الأهمية.
8. الجوانب البيئية والاستدامة
يُعتبر حديد الدكتايل (ASTM A536) أكثر ملاءمة للبيئة مقارنةً بالحديد الرمادي (ASTM A126) نظرًا لانخفاض بصمته الكربونية أثناء الإنتاج وعمره التشغيلي الأطول، مما يقلل من تكرار الاستبدال.
9. المعايير والمعادلات العالمية
| ASTM A126 (الفئة ب) | ASTM A536 (الدرجة 65-45-12) |
|---|---|
| ISO 185 | ISO 1083 |
| BS 1452 | BS 2789 |
| DIN 1691 | DIN 1693 |
تضمن هذه المعادلات استيفاء كلتا المادتين للمعايير الدولية للجودة والأداء.
10. الأسئلة الشائعة (FAQs)
س1: ما هي الاختلافات الأساسية بين ASTM A126 و ASTM A536؟
A1: تكمن الاختلافات الرئيسية في تركيبها الكيميائي وخصائصها الميكانيكية. توفر ASTM A536 قوة شد أعلى وليونة أفضل ومقاومة أفضل للصدمات مقارنةً بـ ASTM A126.
س2: هل يمكن استخدام ASTM A126 في تطبيقات الضغط العالي؟
A2: يمكن استخدام ASTM A126، خاصةً الفئة C، في بعض تطبيقات الضغط العالي. ومع ذلك، يفضل استخدام ASTM A536 في الظروف الأكثر تطلبًا نظرًا لقوته ومتانته الفائقة.
س3: هل اللحام ممكن مع مواد ASTM A126 و ASTM A536؟
ج3: نعم، يمكن لحام كلتا المادتين. ومع ذلك، فإن لحام ASTM A536 يتطلب إجراءات أكثر تخصصًا بسبب قوته وصلابته الأعلى.
س4: كيف تقارن تكلفة ASTM A126 مع ASTM A536؟
A4: ASTM A536 أغلى عموماً من ASTM A126 بسبب خواصه الميكانيكية المحسنة والمعالجة الإضافية المطلوبة.
س5: هل هناك فوائد بيئية لاستخدام ASTM A536 على ASTM A126؟
A5: نعم، تعتبر ASTM A536 أكثر صداقة للبيئة نظرًا لعمرها التشغيلي الأطول وانخفاض بصمة الكربون أثناء الإنتاج.
س6: ما هي المواد المفضلة لتصنيع الصمامات؟
A6: على الرغم من استخدام كلتا المادتين في تصنيع الصمامات، إلا أن ASTM A536 مفضل بشكل متزايد لخصائصه الميكانيكية الفائقة، مما يؤدي إلى صمامات أطول عمراً وأكثر موثوقية.
الخاتمة
باختصار، على الرغم من أن ASTM A126 و ASTM A536 كلاهما معياران للحديد الزهر، إلا أنهما يلبيان متطلبات استخدام مختلفة. تُعد ASTM A126 مناسبة للتطبيقات ذات الأغراض العامة حيث تكون التكلفة عاملاً مهمًا، في حين أن ASTM A536 مثالية للتطبيقات التي تتطلب قوة وليونة ومقاومة أعلى للصدمات. يضمن فهم هذه الاختلافات اختيار المادة المناسبة للاحتياجات الصناعية المحددة.

